Mastering Maize Weevil Control: Protecting Your Crops with Precision

Farming is not just an occupation; it’s a commitment to nurturing and safeguarding the land and its produce. Among the significant threats to maize crops, the maize weevil (*Sitophilus zeamais*) poses a considerable challenge. This article delves into effective strategies for maize weevil control, ensuring that farmers are equipped with the knowledge and tools to protect their harvest.
Understanding the Maize Weevil
Before we explore control methods, it is crucial to understand the biology and behavior of the maize weevil. Here’s what you need to know:
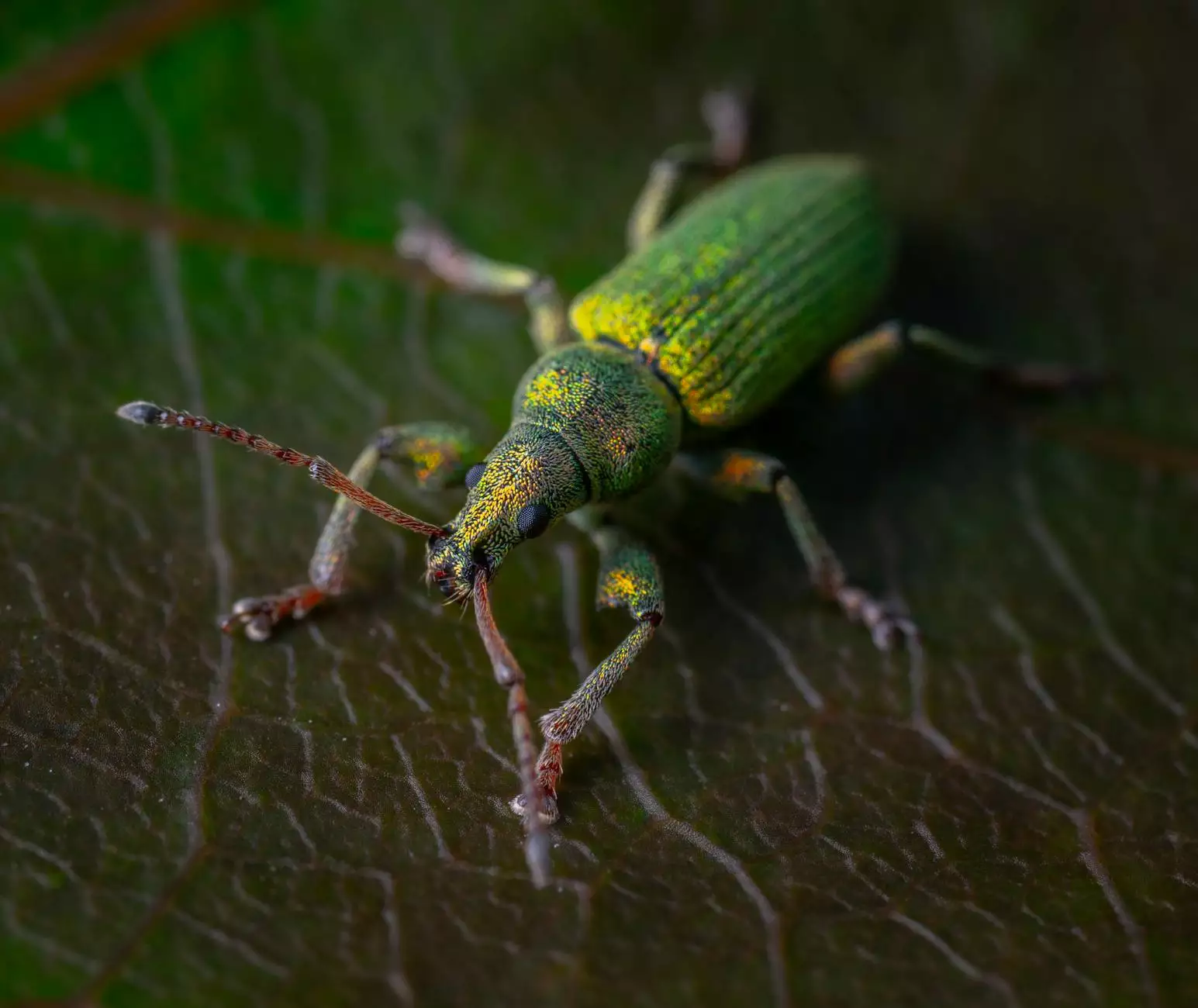
- Identification: Maize weevils are small, dark brown insects, approximately 2-4 mm in length, with a distinctive snout.
- Life Cycle: They reproduce rapidly, with a life cycle of about three to five weeks under optimal conditions.
- Damage Mechanism: Both larvae and adult weevils feed on the kernels, causing considerable damage to the grain.
- Infestation Symptoms: Look for powdery frass, exit holes in the grains, and holes in the maize cobs.
The Importance of Early Detection
Effective maize weevil control begins with early detection. Farmers should regularly inspect stored grains and field crops for signs of infestation. Here are steps to catch the problem early:
- Conduct regular inspections of grain storage facilities.
- Monitor maize fields frequently, particularly around expected harvest times.
- Utilize pheromone traps for early detection.
Integrating Cultural Practices for Control
Employing cultural practices can significantly reduce maize weevil populations. Here are some fundamental approaches:
- Crop Rotation: Rotating crops disrupts the life cycle of maize weevils and other pests.
- Field Hygiene: Keep fields clean and dispose of any crop residues that could harbor pests.
- Timely Harvesting: Harvest maize promptly to reduce the length of time grains are left exposed to weevils.
Physical and Mechanical Control Techniques
Physical and mechanical controls can complement cultural practices. Here are some effective methods:
- Storage Management: Store maize in airtight containers to prevent weevil access.
- Temperature Control: Utilize low temperatures in storage areas, as maize weevils thrive in warmer conditions.
- Physical Barriers: Employ screens and traps to catch wandering weevils.
Chemical Control Measures
When faced with a severe infestation, chemical controls might be necessary. However, caution should be exercised to prevent adverse effects. Here are common pesticides effective against maize weevils:
- Insect Growth Regulators (IGRs): These disrupt the development of weevil larvae, reducing their reproduction.
- Contact Insecticides: Consider using products like pyrethroids for immediate knockdown of adult weevils.
- Systemic Insecticides: Products that can be absorbed by the plant may offer protection, but always follow safety guidelines.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Approach
Employing an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approach can lead to effective long-term maize weevil control. An IPM strategy combines cultural, physical, chemical, and biological methods tailored specifically to the local agricultural environment.
Components of IPM for Maize Weevil Control
- Regular Monitoring: Implement a systematic approach for pest monitoring to determine when interventions are necessary.
- Thresholds: Establish economic thresholds for pest populations to dictate when control measures should be initiated.
- Combining Strategies: Use a blend of control methods as part of your IPM program for the most effective results.
Utilizing Technology in Maize Weevil Control
The advent of technology in agriculture has revolutionized pest control methods. Here are ways technology can enhance maize weevil control:
- Data Analytics: Leverage data analytics for predictive modeling to anticipate weevil invasions based on weather patterns.
- Remote Sensing: Employ satellite imagery for large-scale monitoring to identify affected areas quickly.
- Smart Traps: Use automated traps that can send alerts when weevil presence is detected.
Investing in Quality Farming Equipment
To effectively implement these control measures, investing in high-quality farming equipment is crucial. From harvesting tools to storage solutions, having the right equipment enhances your ability to manage pests efficiently. At TSG C Inc., we offer a wide range of reliable and durable equipment tailored to meet the diverse needs of modern agriculture.
Recommended Equipment for Farmer's Toolbox
- Grain Storage Bins: Essential for protecting harvested maize from weevil infiltration.
- Harvesting Machines: Efficient equipment that minimizes damage during the harvest process.
- Insecticide Application Equipment: Sprayers that ensure the precise and safe application of pest control chemicals.
Empowering Farmers Through Education
Education is a cornerstone of effective pest management. Farmers should continually seek knowledge about emerging research and trends in maize weevil control. Local agricultural extension services provide valuable resources, workshops, and training sessions to empower farmers with the latest best practices.
Recommended Resources for Farmers
- University Extension Programs: Many universities offer research and extension programs focusing on pest management.
- Webinars and Online Courses: Online platforms provide convenient access to expert-led discussions on pest control strategies.
- Local Agricultural Societies: Join local groups to share experiences and gather insights from fellow farmers.
Conclusion: A Unified Approach for Sustainable Maize Weevil Control
Combating maize weevils requires a unified approach that combines knowledge, technology, and robust practices. By integrating cultural, mechanical, and chemical control methods while leveraging modern farming equipment, farmers can mitigate the risks posed by these pests. Ultimately, investing in continuous learning and adopting innovative strategies will lead to greater productivity and sustainability in maize farming. Protect your crops effectively—because a healthy harvest is a commitment to tomorrow’s food security.